The Bittersweet Truth About Sugar
Sugar is a staple ingredient in the modern diet. It’s added to many pre-packaged foods and beverages to enhance flavor and texture. However, consuming too much added sugar can have detrimental health effects. Here’s what you need to know about sugar, its health impact, and how to cut back.
The Issues with Sugar

Sugar tastes great, but it can wreak havoc on our bodies when consumed in excess. Here are some of the main concerns with overdoing sugar intake:
- Weight gain – Sugary foods are high in calories and added sugar is linked to obesity. The body converts excess sugar into fat which leads to weight gain over time.
- Diabetes risk – Frequent sugar spikes from sugary foods put strain on the pancreas and can contribute to insulin resistance, increasing diabetes risk.
- Dental cavities – Sugar feeds oral bacteria which produce acids that erode tooth enamel and cause cavities.
- Inflammation – Research shows added sugars trigger inflammatory responses which are implicated in various chronic illnesses.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease – Excess fructose from sugar has been shown to contribute to fat buildup in the liver.
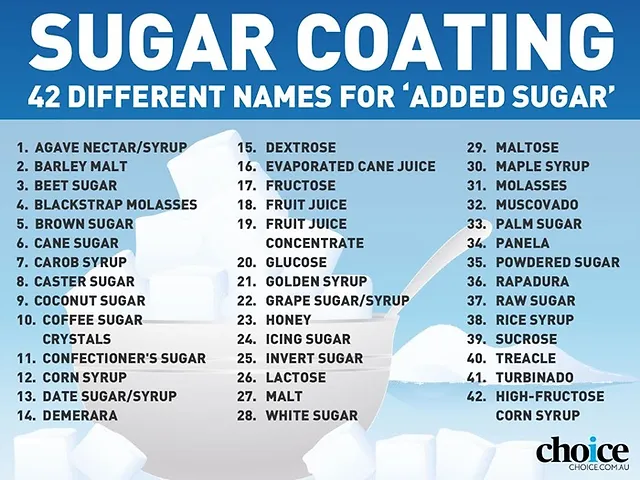
The Many Aliases of Sugar
Food manufacturers use a myriad of different names for added sugars to make ingredients seem healthier than they are. Here are some common sugar aliases to watch out for:
- Syrups: corn syrup, maple syrup, brown rice syrup
- Sugars: cane sugar, beet sugar, raw sugar, turbinado, sucrose
- Sweeteners: agave nectar, honey, coconut sugar, high fructose corn syrup
- Fruit juice concentrates: juices like apple, pear, grape
- Dried fruit: raisins, cranberries, apricots contain natural sugars
Check ingredient lists for these terms which all mean added sugar. Even natural-sounding alternatives like honey and fruit juice contain high amounts of sugar and calories.

Reducing Your Sugar Intake
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to no more than 6 teaspoons (25 grams) per day for women and 9 teaspoons (36 grams) for men. Here are some tips to help cut back on sugar:
- Choose unsweetened beverages like water, tea, and black coffee
- Enjoy fruit instead of sugary desserts to satisfy a sweet tooth
- Buy plain yogurt and add fresh fruit for sweetness
- Limit condiments like ketchup, barbecue sauce, and salad dressings
- Cook at home more often and use little added sugar in recipes
- Opt for savory snacks over cookies, candy, and other sweets
- Check labels and choose low sugar varieties of packaged foods
Be mindful of sneaky added sugars in foods you don’t even consider sweet like bread, tomato sauce, and protein bars. With some simple substitutions and food tweaks, you can enjoy great taste while avoiding sugar overload.
TLDR – Sugar is added abundantly to modern diets, often under misleading names. Consuming excess added sugar can negatively impact health and wellbeing. Limiting sugar intake takes awareness of hidden sugars and choosing healthier alternatives that satisfy your sweet tooth without overdoing empty calories. Small steps to reduce your sugar consumption can have big benefits for your health and waistline.
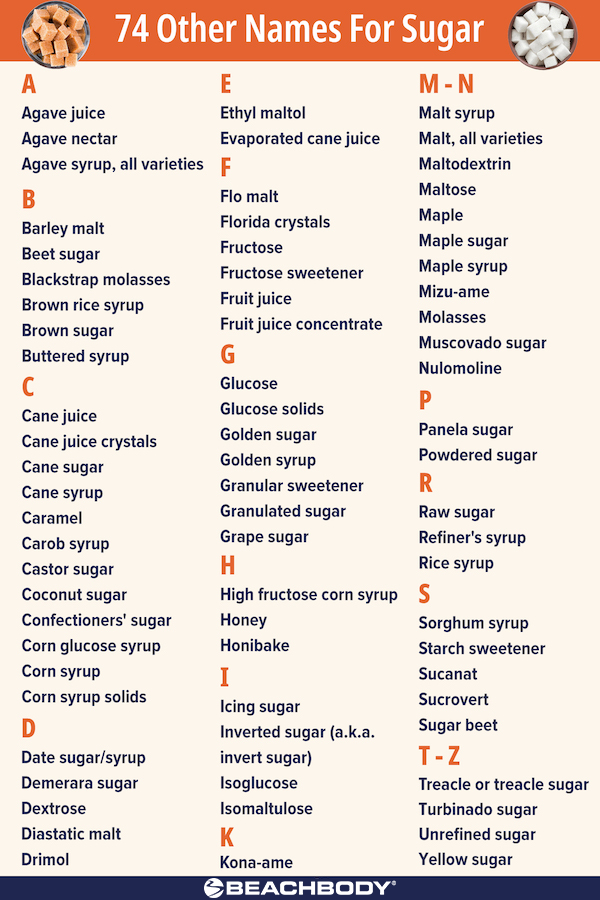
BONUS More Alias of Sugar





 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post